Linux is the operating system that powers over 90% of websites on the internet. If you’ve ever hosted a website before, then you probably have some level of experience with Linux in the form of it’s more user-friendly cousin: cPanel.
To become an expert at cloud computing, however, you’ll have to learn how to operate Linux servers without the help of a graphical user-interface such as cPanel. Although it may sound intimidating at first, getting comfortable with operating Linux servers starts with getting comfortable using the Linux Shell.
What is the Linux Shell/Terminal?
The Linux shell, also commonly referred to as the ‘terminal‘ is the gateway to the back-end of your web server. It uses a ‘command-line-interface’, which doesn’t include the pretty-icons and user friendly experience found in ‘
Getting Started
In this tutorial, you will learn the basic Linux commands for beginners who are getting started in Cloud Computing. Each of the commands listed in this tutorial are the most commonly used commands in the WordPress on Google Cloud tutorials on onepagezen.com.
View by Category
1. User Permissions
-
sudo

sudo command is used to run a single command with root permissions. In the example above, the command sudo is used before the command apachectl restart in order to grant the user the level of permissions required to restart the Apache server.
sudo -i command is used to instill root permissions to the user for the entire duration of the SSH session. Notice how the username changes to ‘root’.2. File and Directory Management
-
touch
-
echo
-
cat
-
mkdir
-
mv
-
ls
-
wget
-
find
-
stat
-
chmod
-
rm

touch is used to create new files. In the example above, the command touch is used to create a new file called myfile.txt in the home directory.
echo is used to insert text into an existing file. In the example above, the command echo "Hello World" >> /home/myfile.txt is used to insert the text “Hello World” into the file called myfile.txt.
cat is used to display the contents of a file in the terminal. In the example above, the command cat /home/myfile.txt is used to display the contents of a file called myfile.txt.
mkdir is used to create new directories. In the example above, the command mkdir /home/mydirectory is used to create a directory called mydirectory inside of the home directory.
mv is used to move files. In the example above, the command mv /home/myfile.txt /home/mydirectory is used to move the file called myfile.txt into the directory called mydirectory. NOTE: Remember to move your myfile.txt file back to the home directory. You can do this by running mv /home/mydirectory/myfile.txt /home

ls is used to list directory contents. In the example above, the command ls /home/mydirectory is used to list the contents of the directory called mydirectory.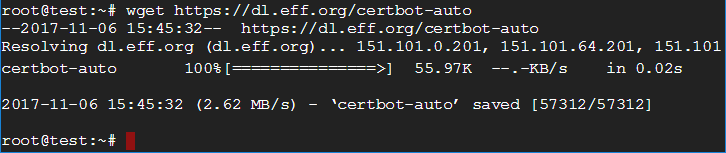
wget is used to download repositories to your Linux machine. In the example above, the command wget https://dl.eff.org/certbot-auto is used to retrieve the certbot-auto repository from eff.org and download it to my virtual machine.
find is used to locate a file or directory. In the example above, the command find / -type f -name wp-config.php is used to locate the file called wp-config.php.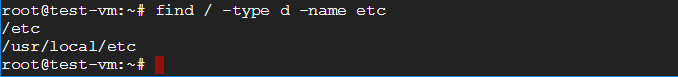
find / -type d -name etc is used to locate the directory called etc.
stat is used to retrieve information about a file or directory. In the example above, the command stat -c "%a %n" /home/myfile.txt is used to find the permission level of the file called myfile.txt.
stat -c "%a %n" /home/mydirectory is used to determine the permission level of the file called mydirectory.
chmod is used to modify file and directory permissions. In the example above, the command chmod 755 /home/myfile.txt is used to change the permission level of the file called myfile.txt to 755.
chmod -R 755 /home/mydirectory is used to change the permission level of the directory called mydirectory to 755. By adding -R, the command becomes recursive, meaning that all of the files contained inside of the directory will inherit the permission changes.
rm command is used to delete a file or directory. In the example above, the command rm /home/myfile.txt is used to delete the file called myfile.txt from the home directory.
command rm -R /home/mydirectory is used to delete the directory called mydirectory and all of it’s contents.3. Apache Server Management
-
apachectl
-
httpd

apachectl command is used to control the behavior of your Apache server. In the example above, the command sudo apachectl start is used to start your Apache server.
sudo apachectl stop is used to stop your Apache server.
sudo apachectl restart is used to restart your Apache server.
sudo apachectl configtest is used to check if your Apache server is configured properly.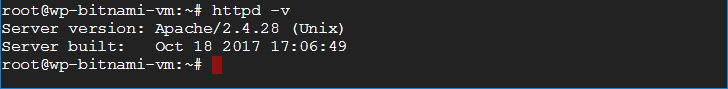
httpd series of commands are used to make changes to your HTTP server, and are oftentimes used interchangeable with the apachectl commands. In the example above, the command httpd -v is used to check the current version of Apache currently running on the server.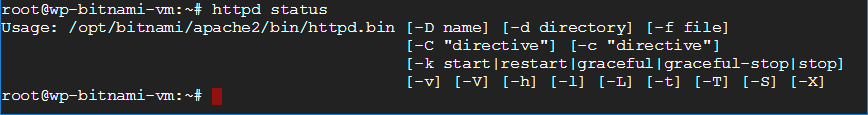
httpd status is used to check the health of your Apache server.Bitnami Apache Server Configurations
-
/opt/bitnami/ctlscript.sh
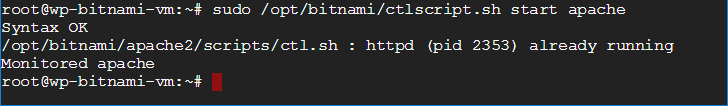
ctlscript is used to control the behavior of your Apache servers running Bitnami stacks, in the same way that apachectl is used in the previous examples. In the example above, the command /opt/bitnami/ctlscript.sh start apache is used to start an Apache server running a Bitnami WordPress stack.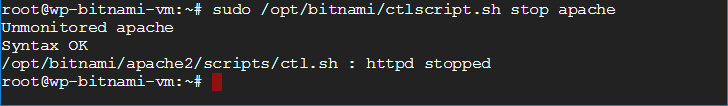
sudo /opt/bitnami/ctlscript.sh stop apache is used to stop an Apache server running a Bitnami WordPress stack.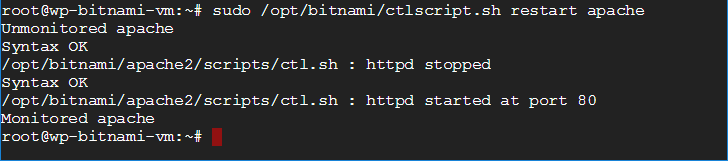
sudo /opt/bitnami/ctlscript.sh restart apache is used to restart an Apache server running a Bitnami WordPress stack.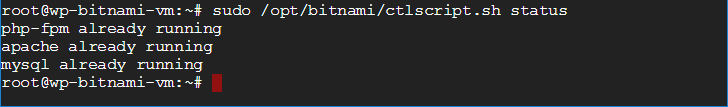
sudo /opt/bitnami/ctlscript.sh status is used to check the health of an Apache server running a Bitnami WordPress stack.4. Virtual Machine Management
-
lsb_release
-
df
-
man
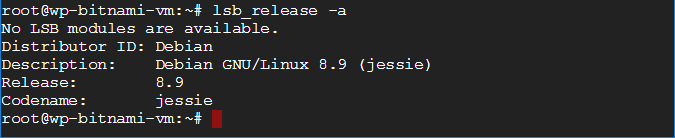
lsb_release -a is used to check the current version of the virtual machine’s Linux operating system.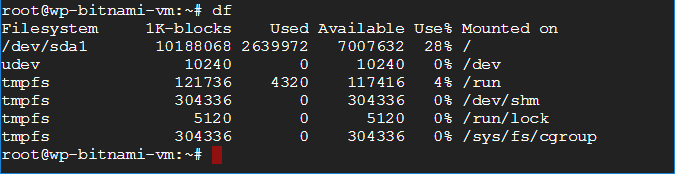
df is used to check the available disk space on a machine.
man command is used to show the different options available for a specific command. In the example above, the command man ls is used to view information about the options available for the ls command.Did it Work?
This is just a small list of the most commonly used Linux commands, there are literally hundreds more!
If you thought of any important commands that were missing from the list, or if you would like to share a question or comment, please post your message below!
Thanks,
![]()
Ahmed Bazuhair says
Hi I can not do anything when I enter sudo telling me it was not connected
Do you have any ideas to solve this problem.
Leron Amin says
Hi Ahmed,
When you enter
sudoit needs to be followed by a command, for examplesudo mkdir jsfileswould make a directory called ‘jsfiles’. Does this answer your question? If not, please share more details about the error message.Thanks,
Joe
Ahmed Bazuhair says
See elcome to Cloud Shell! Type “help” to get started.
was12382 @ endless-cabinet-198419: ~ sudo apachectl restart
sudo: apachectl: The command does not exist
Leron Amin says
Hi Ahemed,
You’re seeing that error because you’re running the command in cloud shell. The command needs to run in the shell that is specific to the VM instance that you wish to connect to.
Navigate to Compute Engine > VM Instances, then click the SSH button next to the instance you wish to connect to.
Hope this helps 🙂
Joe
Ahmed Bazuhair says
root@oilyemen-vm:~# ، stat -c “%a %n” /home/myfile.txt
-bash: ،: command not found
root@oilyemen-vm:~# stat -c “%a %n” /home/myfile.txt
stat: cannot stat ‘/home/myfile.txt’: No such file or directory
root@oilyemen-vm:~# stat -c “%a %n” /home/myfile.txt
stat: cannot stat ‘/home/myfile.txt’: No such file or directory
Leron Amin says
Hi Ahmed,
The file /home/myfile.txt is just an example – this file probably doesn’t exist on your system unless you deliberately created it.
This is why you’re seeing the error message
stat: cannot stat ‘/home/myfile.txt’: No such file or directoryHope this answers your question,
Joe
Benjamin Waller says
Hello Joe,
How are you?
I’ve been looking through is list of commands to find an answer to my current problem but can’t see how to achieve it.
On my Mac, I successfully generated ssh keys via the SSH console from my GCP project and was able to saved the public key in my project inGCP. I watched this video to do that https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=R8C66NwMJLs
However, when i tried to copy the private key from .ssh folder on CGP to my desktop I got the following error: cp: cannot create regular file ‘/home/ben/Desktop/moodle-1_rsa’: No such file or directory. I think I am getting this message because the path in my computer is my system should be ~/home/benjaminwaller/Desktop/moodle-1_rsa
Do you know how i can copy from that key from GCP to my desktop when the username is different? I am trying to construct a command to do it but not sure… Someone like the following:
scp moodle-1_rsa :/Desktop/moodle-1_rsa
I found someone with a similar issue of stackoverflow and am trying to add username@ipaddress of my local desktop. And from the thread below the guy suggested cp -i so I am a bit out of my depth here.
https://stackoverflow.com/questions/27643519/cp-cannot-create-regular-file-users-james-desktop-no-such-file-or-directory
Pls let me know if you know how I should approach this.
Best regards,
Ben
Leron Amin says
Hi Ben,
Configure Google Cloud SDK and generate the SSH keys according to the instructions in this tutorial.
This is the recommended way to secure a connection between your local machine and your Google Cloud project.
Let me know if you have any additional questions,
Joe
Leron Amin says
What did you think about this tutorial?
Share your questions and comments!